The GSM network architecture is a fundamental aspect of mobile communication systems, enabling seamless voice and data services globally. In this article, we will delve deep into the intricacies of GSM, exploring its components, functionalities, and the role it plays in the mobile communication landscape. Whether you are a telecommunications student, a professional in the field, or simply someone intrigued by mobile technology, this guide aims to provide a thorough understanding of GSM network architecture.
With the rapid evolution of mobile technologies, understanding the underlying architecture of GSM is crucial. The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) has shaped mobile networking since its inception in the 1980s, and its principles continue to influence modern communication systems. As we navigate through this article, we will cover various aspects of GSM, including its history, architecture, and the advantages it offers. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how GSM operates and its significance in today’s technological environment.
Let's embark on this journey to explore the fascinating world of GSM network architecture, uncovering the complexities and innovations that have made mobile communication an integral part of our lives.
Table of Contents
- 1. History of GSM
- 2. Overview of GSM Network Architecture
- 3. Key Components of GSM
- 4. Functions of GSM Network Elements
- 5. Advantages of GSM Technology
- 6. Challenges Faced by GSM
- 7. The Future of GSM and Mobile Networks
- 8. Conclusion
1. History of GSM
The development of GSM dates back to the early 1980s when the need for a standardized mobile communication system became evident. Before GSM, mobile communications were based on various incompatible systems, leading to fragmented services. The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) was tasked with creating a new standard that would unify mobile communication across Europe.
In 1982, ETSI initiated the GSM project, which aimed to develop a digital mobile communication system that would support voice and data transmission. The first GSM call was made in 1991, marking a significant milestone in mobile technology. Since then, GSM has evolved, becoming the most widely used mobile communication standard worldwide, with billions of subscribers.
2. Overview of GSM Network Architecture
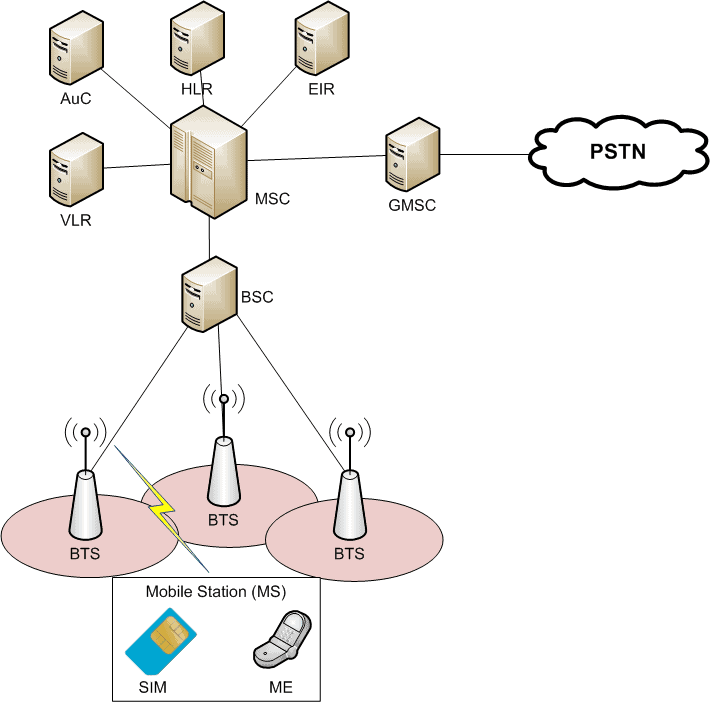
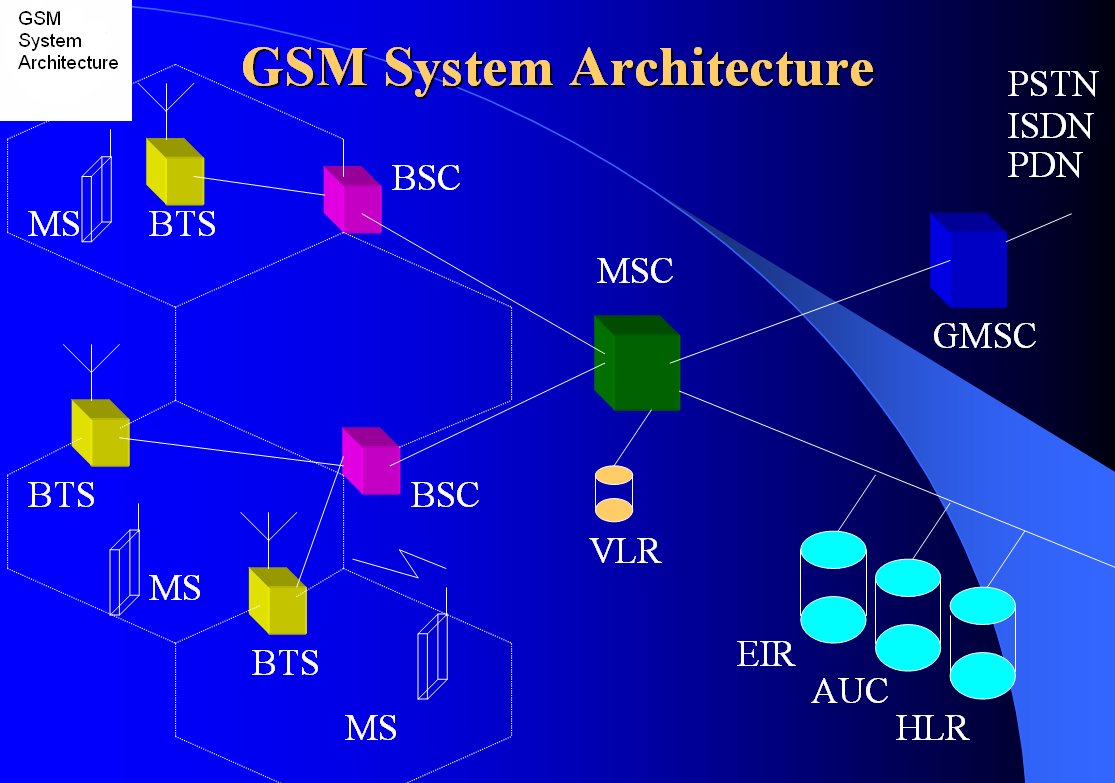
The GSM network architecture is designed to support various services, including voice calls, SMS, and data services. It is structured into several key components that work together to provide seamless communication. The architecture can be categorized into three main subsystems:
- Mobile Station (MS)
- Base Station Subsystem (BSS)
- Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS)
2.1 Mobile Station (MS)
The Mobile Station (MS) comprises the mobile device itself and the Subscriber Identity Module (SIM). The SIM card contains essential information about the subscriber, including their phone number and network identity. The MS is responsible for initiating and receiving calls, sending messages, and accessing data services.
2.2 Base Station Subsystem (BSS)
The Base Station Subsystem (BSS) consists of the Base Transceiver Station (BTS) and Base Station Controller (BSC). The BTS facilitates radio communication with the mobile stations, while the BSC manages the radio resources and controls multiple BTS units. The BSS is crucial for handling the radio interface and ensuring efficient communication between the MS and the network.
2.3 Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS)
The Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS) is responsible for call routing, switching, and managing connections between mobile stations and external networks. It includes components like the Mobile Switching Center (MSC), Home Location Register (HLR), and Visitor Location Register (VLR). The NSS plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of mobile communication.
3. Key Components of GSM
Understanding the key components of GSM is essential for grasping its functionality and operational capabilities. Here are the main components:
- Mobile Switching Center (MSC): The MSC is the core component of the NSS, responsible for call processing, mobility management, and routing calls to other networks.
- Home Location Register (HLR): The HLR is a central database that stores subscriber information, including user profiles, service subscriptions, and current location.
- Visitor Location Register (VLR): The VLR is a temporary database that stores information about subscribers currently within the coverage area of the MSC.
- Base Transceiver Station (BTS): The BTS is the hardware that enables wireless communication with mobile devices, handling radio frequency signals.
- Base Station Controller (BSC): The BSC manages multiple BTS units, controlling their operation and allocating resources for efficient communication.
- Mobile Station (MS): The MS includes the mobile device and SIM card, responsible for user interaction and communication with the network.
4. Functions of GSM Network Elements
Each component of the GSM architecture has specific functions that contribute to the overall operation of the network. Here’s a detailed look at the functions of key elements:
4.1 Mobile Switching Center (MSC)
- Call setup and teardown
- Mobility management, including location updates
- Interfacing with other networks (PSTN, ISDN)
4.2 Home Location Register (HLR)
- Storing subscriber information and service profiles
- Managing subscriber mobility and location data
- Facilitating service provisioning and authentication
4.3 Visitor Location Register (VLR)
- Maintaining temporary subscriber data
- Providing quick access to subscriber information for active users
- Reducing the load on the HLR for frequently accessed data
5. Advantages of GSM Technology
GSM technology offers several advantages that have contributed to its widespread adoption:
- International Roaming: GSM allows users to use their mobile devices across different countries with ease, making it convenient for travelers.
- High Call Quality: GSM provides enhanced voice clarity and reduced call drop rates due to its digital nature.
- Security Features: GSM incorporates encryption and authentication mechanisms to protect user data and communication.
- Support for Multiple Services: GSM supports not only voice calls but also SMS and data services, enabling a range of applications.
6. Challenges Faced by GSM
Despite its many advantages, GSM technology also faces certain challenges:
- Limited Data Speeds: GSM is primarily designed for voice communication, and its data transfer rates may not meet the demands of modern applications.
- Network Congestion: As the number of users increases, network congestion can occur, leading to dropped calls or slower data speeds.
- Compatibility Issues: Newer technologies like 3G and 4G may create compatibility issues for GSM networks, requiring upgrades and adaptations.
7. The Future of GSM and Mobile Networks
As mobile technology continues to evolve, the future of GSM and mobile networks is promising. The introduction of newer standards like LTE and 5G will enhance data speeds and network capabilities. However, GSM will still play a crucial role, especially in areas where newer technologies are not yet deployed.
Moreover, the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) with GSM networks opens up new possibilities for smart devices and applications. The ongoing development of mobile technologies ensures that GSM will adapt and remain relevant in the ever-changing landscape of telecommunications.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, the GSM network architecture is a cornerstone of mobile communication, enabling millions of users to connect globally. By understanding its components, functions, and advantages, we gain insight into the technology that powers our daily communication. As we look to the future, the evolution of GSM alongside newer technologies will shape the way we connect and communicate.
We invite you to share your thoughts on GSM technology in the comments below. If you found this article informative, consider sharing it with others who may benefit from a deeper understanding of GSM network architecture
Baddiestv: The Rise Of A Social Media Phenomenon
HD Hub 4U: Your Ultimate Source For High-Definition Content
Adriane Love Biography: A Journey Through Her Life And Career
What is GSM and How does it Work? Electrical Technology

Learn about basics and Smartcities GSM Core Network Diagram
Its My Skill GSM System Architecture